#1 What is laser embossing?
Laser embossing is to use laser beams to carve a design on the material surface. To create a raised effect, the bitmap design is first divided into multiple layers, and then the laser follows specific settings to cut the layers into different depths.
#2 Preparations
Connect xTool F1 Ultra to XCS
Follow the instructions in Connect xTool F1 Ultra to XCS on the Computer.
How to prepare a design for laser embossing?
To laser emboss a material, you need to use a depth map as the processing object.
Depth maps
In 3D computer graphics and computer vision, a depth map is an image or image channel that contains information about the distance of objects from a specific perspective or reference point. Each pixel is assigned a value to represent the distance of that pixel from the reference point, which creates a 3D representation of the scene for its RGB image or virtual scene.

The Stanford Bunny above is a depth map. The white pixels represent the part of the scene that is closest to the reference point, and the black pixels represent the part of the scene that is furthest. In this case, the parts of the scene that are closest are the ears of the bunny. The grayscale gradient in between illustrates that the head, neck, and body are a bit further from the reference point, the legs even further, and the tail of the bunny the furthest before the background, or furthest point of the image. When processing, the dark color is the deep part of the engraving, and the light color is the shallow part of the engraving.
How to obtain a depth map
You can obtain a depth map from the following channels:
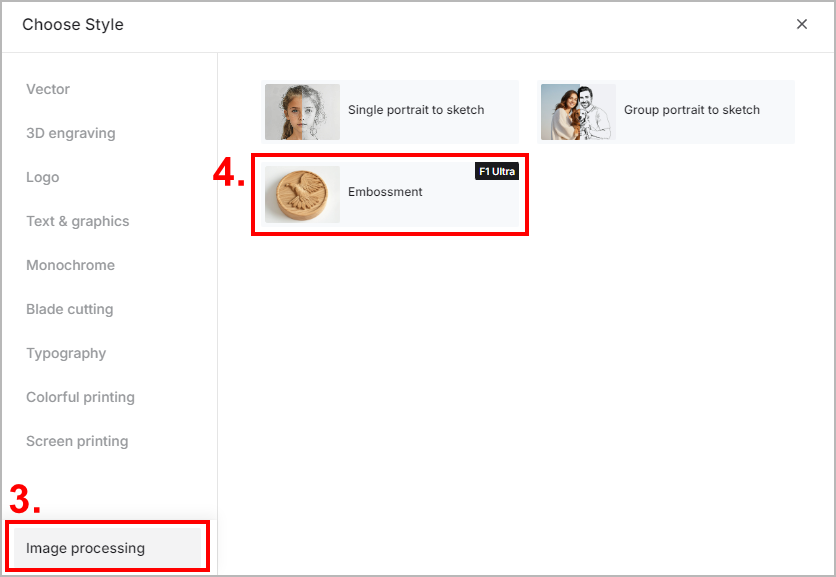
- Generate a depth map in xTool AImake
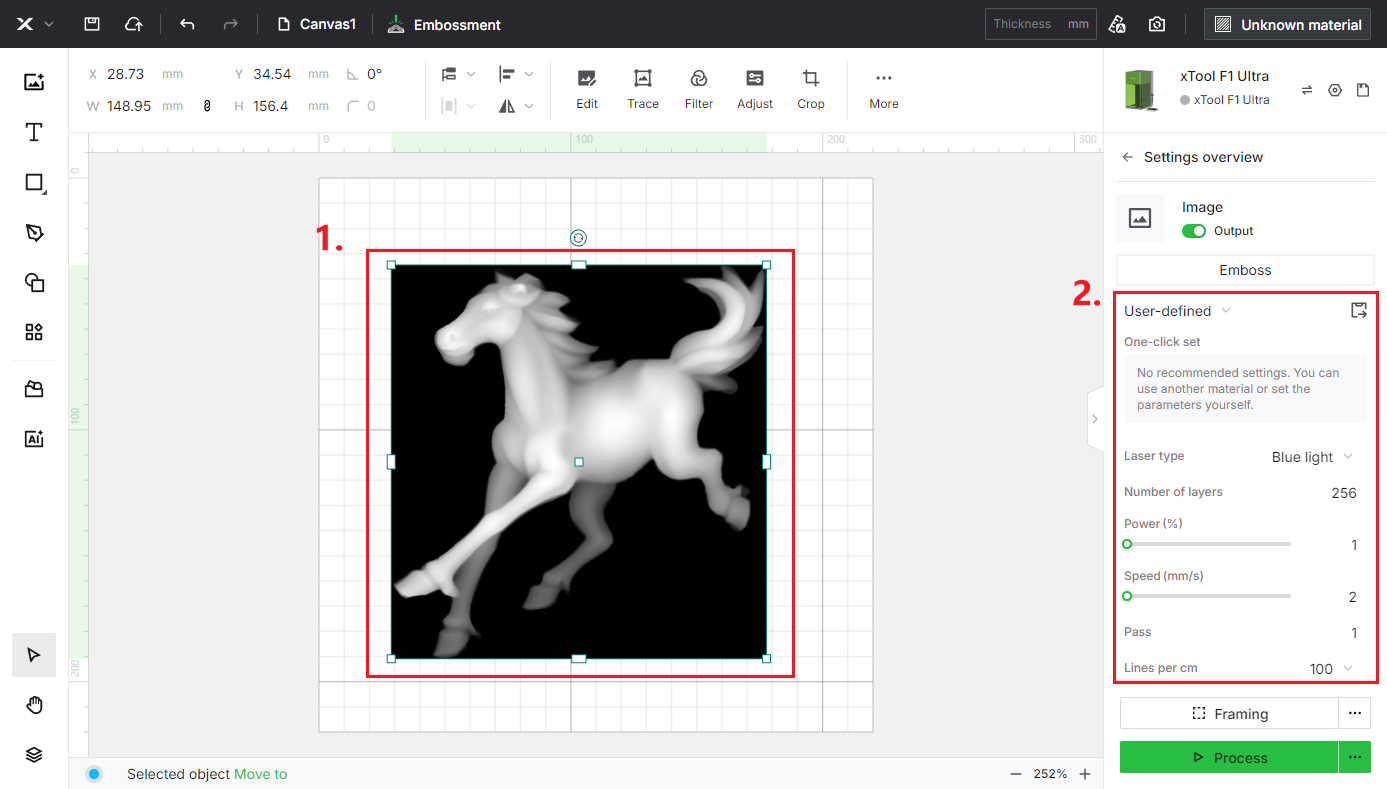
(1) On the left side of the project editing page in XCS, click the icon > the current style name. Then, select Image processing > Embossment.
icon > the current style name. Then, select Image processing > Embossment.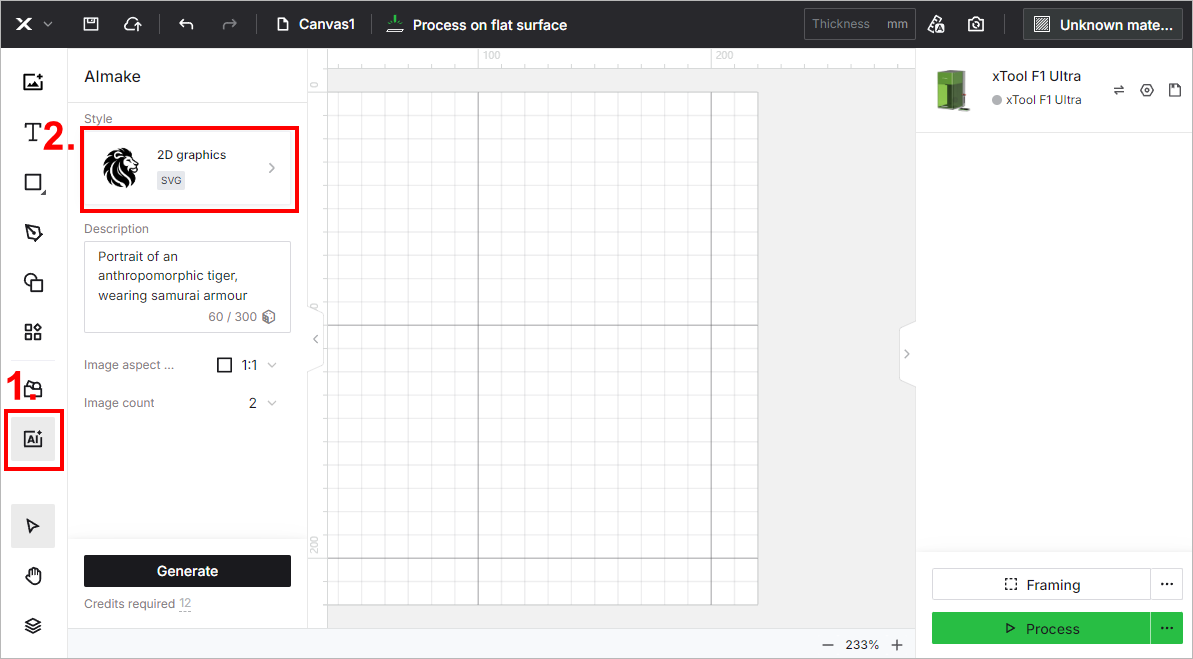

(2) Upload an image, and enter a prompt if needed. Then, select Emboss or Deboss. At last, click Generate to generate a depth map.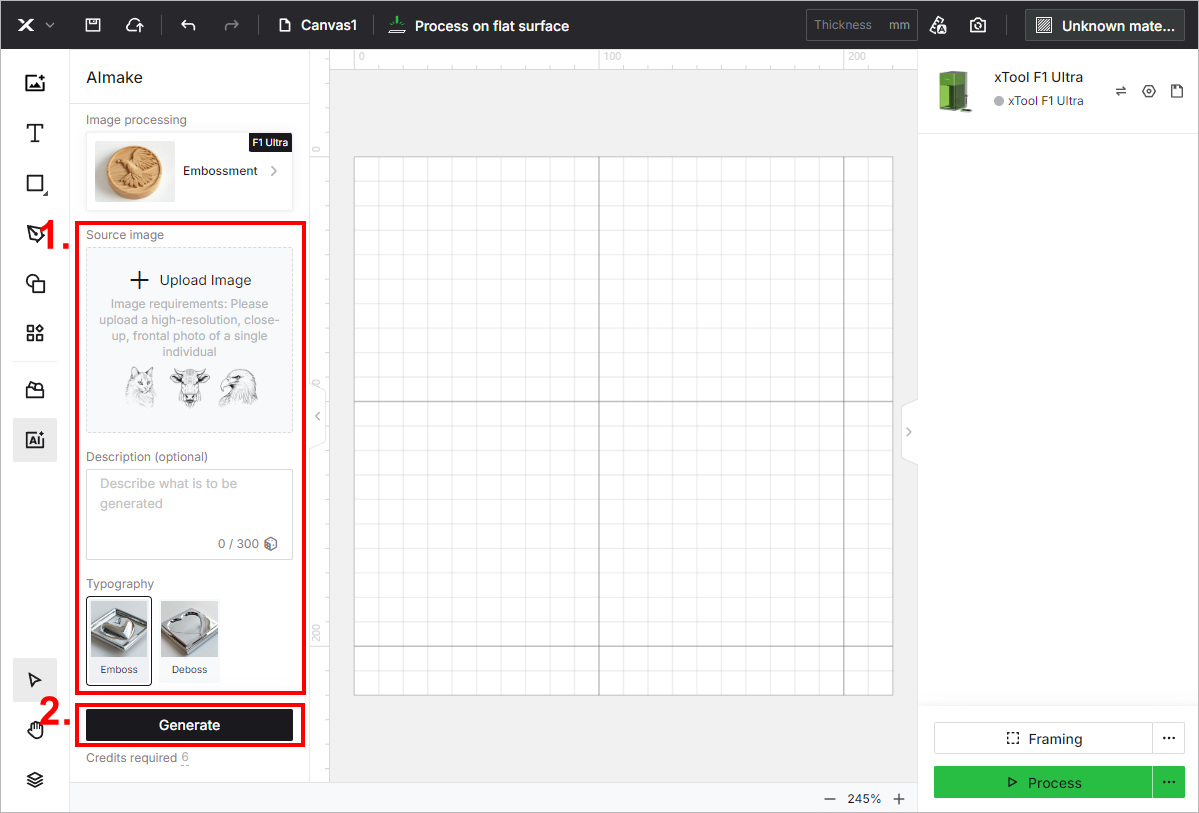
- Select a depth map from Shape
On the left side of the project editing page in XCS, click the icon. Scroll down to find Embossment and select a depth map under this category.
icon. Scroll down to find Embossment and select a depth map under this category.
|
- Import a depth map
You can download a depth map from the Internet or create one in third-party software, and then import the image to XCS.
On the left side of the project editing page, click the icon to import a depth map.
icon to import a depth map.
|
#3 Start laser embossing
1. Select the processing mode and material name
(1) On the top of XCS, click the name of the current processing mode, and then select Embossment as the processing mode.
|
(2) In the top-right corner, click User-defined material, select the name of your material, and click Confirm.
|
2. Place the material and perform laser focusing
(1) Lift the protective enclosure, and place the material on the baseplate, allowing the blue light spot to fall on the surface of the material.

(2) Hold down on the Up/Down button for laser module to lift or lower the laser module. When the red and blue light spots overlap, the focus is successfully set.



After you finish focusing, you can see the measured material thickness in the top-right corner of XCS.
|
3. Shoot background and import a depth map
(1) In the top-right corner of XCS, click the Refresh background icon .
.
|
(2) Use the methods described in How to obtain a depth map to import a depth map.
For example, on the left side of XCS, click > Embossment > select a depth map to import it.
> Embossment > select a depth map to import it.
|
(3) Resize or move the image. Drag the anchor points of the bounding box to resize the image, and drag the image to move it.
|
4. Set processing parameters
Select the object on the canvas. On the right side of XCS, set parameters for the object.
|
- Laser type
- Blue light is typically used with materials like Tilia wood, corrugated paper, and leather, and for laser cutting.
- Fiber IR is ideal for engraving metals such as stainless steel, gold, silver, copper, aluminum, etc.
- Number of layers
The more layers you set, the deeper the laser carves into the material surface. Valid value: [1, 256], integer.
- Power (%)
The power of the laser. The higher the power, the deeper the laser carves into the material surface. Valid value: [1, 100], integer.
- Speed (mm/s)
The moving speed of the laser dots along the processing path. If the laser dots move slower, the processing time will be longer and the material will absorb more energy. Therefore, the smaller the speed, the deeper the laser carves into the material surface.
- Pass
The number of times the laser dots pass over the processing path. The more passes, the deeper the laser carves into the material surface. Valid value: [1, 10], integer.
- Lines per cm
The number of lines engraved within each centimeter. It affects the resolution of the embossing result.
- Engraving angle
The angle of the laser beams when engraving on the material. This angle is a relative angle between the laser beams and the processing points. For normal operation, it is recommended to set the value to 30.
- Descend at the z-axis
As the laser carves deeper into the material, the laser beam may be out of focus. By turning on this feature, the laser module will descend at the z-axis, so that the laser beam can keep focusing on the material surface. A focused laser beam produces the highest energy.
For materials such as brass that require high laser power, you are advised to turn on Descend at the z-axis for better processing results. In other conditions, if not necessary, you are not advised to turn on this feature.
5. Set the processing path
In the bottom-right corner of XCS, click the icon to set the processing path.
icon to set the processing path.
|
(1) Turn on or off the Evade smoke mode.
When this feature is enabled, the device follows a path less affected by the smoke to process the material.
(2) Set the Processing path.
- Auto planning: XCS automatically plans the processing path based on intelligent algorithms.
- User defining: Manually set the processing paths for some objects.
6. Preview the processing area
You can preview the processing area on the material by framing. Framing means laser dots walk along the border of the processing objects on the material. Take the following steps to start framing:


● Light power: Sets the laser power for framing.
● Mode:
In the Rect mode, laser dots walk along the rectangle border of the processing objects.
In the Outline mode, laser dots walk along the outline of the processing objects.
(2) Click Framing in the software. The laser dots will move along the boundary of the processing objects on the material, allowing you to preview the processing area.

To stop framing, click the Stop Framing button in the bottom-right corner of XCS.

7. Start processing
(1) In the bottom-right corner of the software, click Go to process.
|
(2) Preview the processing design.

(3) Close the protective enclosure of xTool F1 Ultra. In the upper right corner of XCS, click Start. When the software shows “Ready”, press the XTOOL Start/Stop button on the touchscreen controller to start processing.


Notes
- After laser embossing a metal, if the processing result has a dark color, you can try laser engraving the work with one more pass.
- Ensure that you use a clear image for laser embossing.

Services & Help
Learn & Community
Copyright © 2025 xTool All Rights Reserved.