xTool-recommended materials and parameters
Click here to view online the latest version of xTool-recommended materials and related parameters for xTool MetalFab CNC Cutter. To download the table, click here instead.
Parameter descriptions
The following explains the parameters mentioned in the link, which are factors that affect the final cutting results.
Shielding gas
Gas type | Description | Note |
|---|---|---|
Oxygen | ✔ Enhancing combustion ✔ Faster cutting process ✔ Suitable for cutting carbon steel and galvanized sheet with a thickness of 2mm or more ❗Edge oxidation |
|
Nitrogen | ✔ Oxidation-proof ✔ Suitable for cutting stainless steel, aluminum, and brass | |
Argon | ||
Compressed air | ✔ Low cost ✔ Suitable for stainless steel, aluminum, brass, as well as carbon steel and galvanized sheet thinner than 2 mm |
Gas pressure
Gas pressure affects cutting speed and dross removal. Specifically, low gas pressure may lead to remaining dross, while high gas pressure may disturb the stability of laser beam.
- Do not exceed the maximum gas pressure for the device.
- xTool Air Compressor related (for details, visit xTool Air Compressor & Air Dryer FAQs)
- Dross may appear when cutting 3 mm or 4 mm aluminum with 0.6 MPa gas pressure
- 5 mm stainless steel cannot be cut with high gas pressure using SaveGas™ nozzle.
Nozzle type
Nozzle | Image | Description |
|---|---|---|
Ordinary nozzle |
| ✔ Single-layer gas channel ✔ Cutting thin carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, brass ❗Cutting only thin metal when gas pressure < 1.2 MPa ❗Poor air flow concentration, susceptible to external interference ❗Dross appears when cutting thick metal, which affects processing results |
Double-layer nozzle |
| ✔ Dual-layer gas channels
✔ Suitable for cutting with special gas such as oxygen or nitrogen |
SaveGas™ nozzle |
| ✔ Thick metal cutting ✔ Uniform cutting surfaces ✔ Strong interference resistance ✔ Stable cutting during high-speed movement |
Nozzle diameter
The nozzle diameter refers to the size of the nozzle opening, which affects the gas flow concentration and pressure distribution.
- Smaller diameter: ideal for cutting thin plates, as the gas flow is more focused. In oxygen cutting, a smaller nozzle diameter results in a more concentrated gas flow, improving combustion.
- Larger diameter: better for thick plates, as it creates a larger gas flow area to assist cutting. However, if the diameter is too large, the gas flow may become too dispersed, reducing efficiency.
To ensure optimal cutting results and operation safety, recalibrate the focus position after you replace a nozzle with a larger-diameter one.
- Diameter size: Double-layer nozzle < Ordinary nozzle < Telescopic cutting nozzle < CNC cleaning nozzle
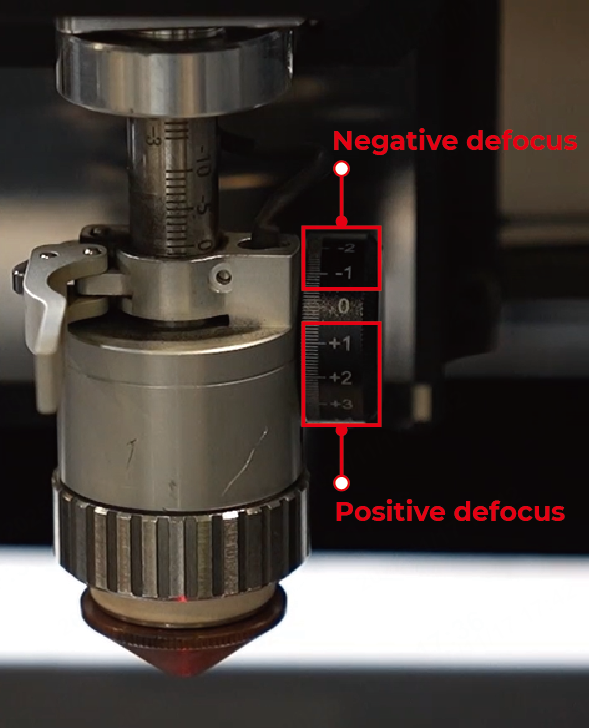
Defocus amount
Defocus amount refers to the distance between the laser focus and the material surface, which affects the red spot size and energy density.
Focus type | Illustration | Focus position | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Negative defocus |
| Inside the material | The red spot is small and the energy is strong, suitable for thick metal processing. |
Positive defocus | Above the material | The red spot is large and the energy is weak. |
Following height
The following height refers to the distance between the nozzle and the material surface.
Appropriate distance ensures that the shielding gas efficiently removes dross. However, long distance diminishes dross removal effects, while short distance may lead to nozzle collision.
Power
Laser power affects cutting speed and processing results. Excessive power may cause ablation, while insufficient power may fail to cut through the material.
Duty cycle
The percentage of time a device is active or "on" during one complete cycle. Value range: 0–100%
High duty cycle means high energy input, which may lead to overheating. Low duty cycle is suitable for precise cutting, minimizing thermal distortion.
Frequency
Laser pulse frequency (Hz) per second affects cutting speed and processing quality of material edge.
High frequency works for thin metal cutting, producing smoother cut surfaces, while low frequency is suitable for thick metal cutting, delivering higher single-pulse energy but potentially resulting in rougher edges.
In normal cases, the setting of frequency requires coordination with that of duty cycle.
Speed
The moving speed of the laser module also affects the cutting results. Fast cutting often leads to incomplete cutting, while slow cutting results in low efficiency and thermal deformation of materials.
Curves for duty cycle and frequency
There're two curves in xTool software: one is for duty cycle adjustment, the other is for frequency adjustment. When processing intricate patterns or corners, bringing down duty cycle or frequency can reduce overheating or dross build-up.
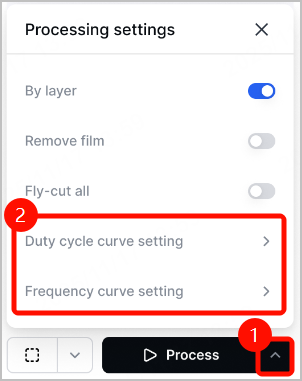
Note: For more information, visit xTool MetalFab CNC Cutter Processing Curve Adjustment Tutorial.
Acceleration
The acceleration of the laser module affects the cutting results. High acceleration boosts efficiency, yet may bring down precision and stability.
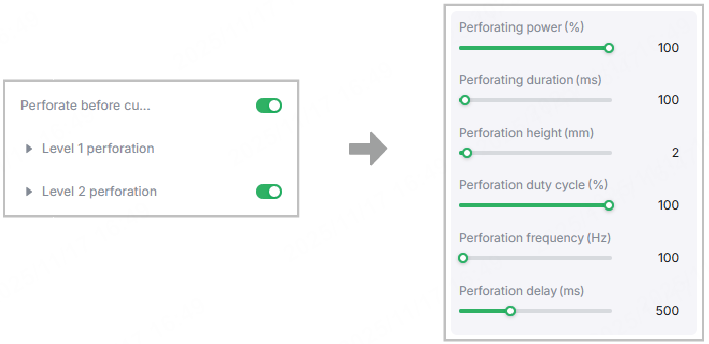
Perforation
Perforation is a step before cutting. To avoid excessive perforation depth which causes sparks, it's recommended to divide perforation into two phases.
Level 1 perforation often comes with high power and high speed. Level 2 perforation, on the other hand, gives us a chance to adjust settings for better perforation and less dross build-up. Speaking of settings, they are composed of power, duty cycle, frequency, and speed. All of these parameters affect the time and quality of perforation and help to prevent sparks and burn-through.
In addition, Perforation delay in xTool software refers to the waiting time after a perforation task. The waiting time is necessary for molten material removal, which helps to avoid poor quality at the cutting start point.
Soft start
Soft start refers to a slow and controlled start of the device's motion to improve the quality and precision of the cut.
For some thick materials, if the cutting start point shows dross, slagging, or poor perforation after adding the lead-in, you can enable Soft-Start in xTool software and adjust its distance, speed, and height for better results.

Services & Help
Learn & Community
Copyright © 2025 xTool All Rights Reserved.